
Dr. Gopala Krishna Behara
Introduction
Today, Generative AI (GenAI) technology has become so disruptive and changing the way enterprises do business and introducing new risks. In any recent seminars, conferences on IT technology, the leaders always mention the benefits of the usage of “Generative AI”.
Enterprises need to understand disruptive technology and the trends to properly develop a strategy for leveraging Generative technology successfully. The focus of business-driven AI strategy is to maximise the benefits and minimize the risk associated with AI based solutions. Identify the opportunities to enhance business outcomes by developing and deploying AI applications. The GenAI Strategy requires to be:
- Business driven and aligned to the enterprise strategy
- Guiding Principles to increase the efficiency, improve decision making, reduce cost and increase the revenue for the enterprises
- Automate the business processes to achieve better business value
- Faster product development, enhanced customer experience and improved employee productivity
- Roadmap to deliver and support new AI-based solutions to realize the enterprise use cases
This paper covers the industry adoption of Generative AI technology, Generative AI strategy approach, best practices of Generative AI.
Industry Adoption of Generative AI
According to Gartner, “Any organization in any industry, especially those with very large amounts of data, can use AI for business value.” Generative AI is primed to make an increasingly strong impact on enterprises over the next five years.
- By 2025, 30% of enterprises will have implemented an AI-augmented development and testing strategy, up from 5% in 2021 – Gartner
- By 2026, generative design AI will automate 60% of the design effort for new websites and mobile apps – Gartner
- By 2027, nearly 15% of new applications will be automatically generated by AI without a human in the loop. This is not happening at all today – Gartner
- Recent CEO surveys show almost 80% of CEOs believe AI is likely to significantly enhance business efficiencies in their organization – Forbes
- Today, an estimated 60% of IT leaders are looking to implement Generative AI – CIO.com
- Generative AI is rated to be the top emerging enterprise technology. 80% believe that it will disrupt their industry and nearly all (93%) think generative AI will provide value to their business – KPMG
- Generative AI coding support can help software engineers develop code 35 to 45 percent faster, refactor code 20 to 30 percent faster, and perform code documentation 45 to 50 percent faster-McKinsey
- 44% of the worker’s core skills are expected to change in the next five years. Training employees to be able to leverage Generative AI is going to be critical – World Economic Forum.
Business Case for Generative AI Strategy
Many CXO’s see the IT budget as an area of overspending and are continuously looking for ways to reduce costs and effort.
Driving business outcomes with GenAI requires strategy and collaboration from enterprise teams. Bring all the business stakeholders together to develop the enterprise AI Strategy, vision, and objectives. Establish GenAI principles to guide AI investments and deployments. The following strategy level questions help to understand about the enterprise readiness for the GenAI adoption.
- Is there a CXO mandate for Generative AI?
- Is there a top management-level charter for Generative AI tied to one or more of the drivers?
- Do enterprise has a published Business Strategy for Generative AI?
- How does the Generative AI help in enhancing existing processes and enterprise strategy?
- Is there an internal business case built? If so, at what level?
- Does the workforce possess the skills to use Generative AI, and what are the implications for talent acquisition and upskilling?
- What risks emerge when deploying Generative AI and how do these risks impact Generative AI value?
Challenges in Implementing Generative AI
Enterprises face significant customization, performance and security challenges when implementing GenAI solutions. The more prominent challenges are:
- Enterprises have proprietary data and unique needs that require extensive fine tuning of base foundation models and prompt engineering
- Poor trained base models that hallucinate, respond users with false, harmful or unsafe results requiring continuous evaluation and monitoring by experts
- Cloud models can leak proprietary data. IP, PII and model interaction history and pose other security and safety risks
Generative AI Strategy Approach
An effective GenAI strategy is driven by the business stakeholders of the enterprise and focused on delivering improved business outcomes. The Key business drivers need to focus on:
- Better customer experience
- Increasing revenue
- Reducing cost
- Improving time to market
- Reducing risk
Define clear vision for GenAI implementation through product or homegrown. Incorporate GenAI guiding principles and standards for implementation. Decide on buy, build, borrow, bridge LLMs. Socialize GenAI across Organization. The key components of GenAI strategy are,
- Vision and Mission
- Strategy Guidelines
- Guiding Principles
- GenAI initiatives
- Implementation roadmap
The following diagram depicts the Generative AI strategy approach to be adopted across the enterprise.
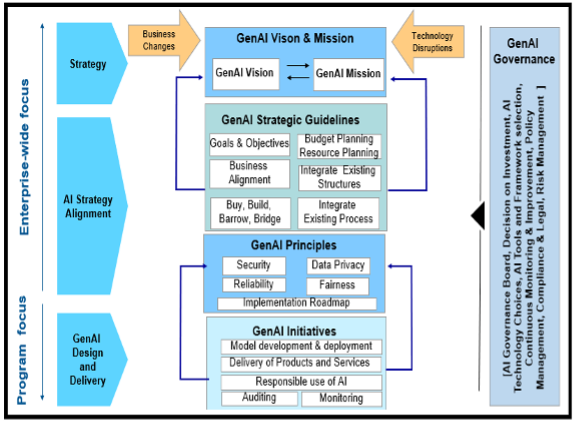
Figure 1: Generative AI Strategy
GenAI Vision & Mission: Define a clear vision and mission for GenAI implementation aligned with the enterprise goals and business Strategy. An effective AI vision of an enterprise is forward-looking and aspirational and reflects the enterprise’s commitment to leveraging AI to deliver positive and responsible outcomes.
The Mission of GenAI is to harness the power of GenAI technologies to support and drive enterprise innovation, efficiency, growth, and resilience. Also strategically integrate GenAI into business operations through business aligned initiatives and maintain secure and high-quality data.
GenAI Strategy Guidelines: The guidelines to align with enterprise business Initiatives. Identify the business challenges that require attention. Also, understand the business benefits of AI adoption that are critical for the success of enterprise. Select the targeted use cases and perform the Proof of Concepts (POC) that can deliver desired business and operational outcomes. AI use cases should not be viewed in isolation. AI initiatives and technology should be integrated into existing business processes and workflows to optimize and streamline them. Build value through improved productivity, growth, and new business models.
AI initiatives must deliver business value and align with the enterprise strategic objectives. Prioritize AI use cases that enable or create business capabilities aligned with the enterprise’s key initiatives.
GenAI Principles: GenAI encompasses the design, development, and monitoring of artificial intelligence systems to augment and enhance the productivity and quality of work across enterprises. Top 6 GenAI principles and Rationale are described below:
- Principle 1: People should be accountable for AI systems.
- Rationale: Create an oversight so that humans can be accountable and in contact. Assess the impact of the system on people and organizations.
- Principle 2: AI Systems should be transparent and understandable.
- Rationale: Design AI systems to intelligently for the decision making. AI systems are designed to inform people that they are interacting with an AI system.
- Principle 3: AI systems should treat all people fairly.
- Rationale: AI systems are designed to provide a similar quality of service for identified demographic groups
- Principle 4: AI systems should empower everyone and engage people.
- Rationale: AI systems are designed to be inclusive in accordance with enterprise accessibility standards
- Principle 5: Design systemic data quality management
- Rationale: Integrate data from numerous systems into a unified federated data. Data must be current and real-time. Train data be available for the enterprise AI systems. Define data access controls, data sharing agreements, data life cycle management procedures for GenAI systems.
- Principle 6: Provide enterprise data governance and security.
- Rationale: Generative AI platform must provide robust encryption, multi-level user access authentication, and authorization controls.
Build GenAI Implementation Roadmap: Discuss with key stakeholders and SMEs and review documentation and current GenAI initiatives. Assess GenAI current Maturity of the enterprise across different maturity levels. Important Maturity dimensions include AI Governance, Data Management, People, Process and Technology capabilities.
GenAI Initiatives: Prioritize GenAI usecase initiatives based on highest potential value and feasibility to execute. Implement model development lifecycle that includes products and services, rigorous testing, validation, and documentation. Build Roadmap that provides a plan to deliver the identified GenAI applications by prioritizing and simplifying the actions required to deliver identified initiatives. Create processes for ongoing monitoring and auding of GenAI systems for responsible use of AI to ensure compliance with legal, ethical standards and algorithmic biases.
Generative AI Governance: Setup Generative AI Governance across enterprise. Define roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in GenAI development, deployment, and monitoring. Foster the collaboration between AI experts, domain experts and business stakeholders. Establish a centralized, cross-functional team to review and update GenAI governance practices as technology, regulations, and enterprise needs. Conduct risk assessments to identify potential risks associated with GenAI implementation. Formulate communication mechanism for stakeholders to understand GenAI technologies and their implications.
Evaluating GenAI tools for the enterprise business. The tool needs to adhere to the enterprise standards like security, privacy, data handling and compliance. The tool needs to empower the stakeholders to deliver business needs and continuously improve the experiences it generates against business metrics.
- Establish Workforce: Educate employees in the usage of GenAI technologies, their usage across enterprise systems, challenges of usage of GenAI and how to overcome them. Conduct structured training to build new skills and apply new ways of thinking that deliver better experiences to end users. Formulate communication mechanism for employees to understand GenAI technologies and their implications.
Reskill the employees to improve productivity by conducting various training courses and encourage them to perform POCs. Also, based on role and skills of employees, identify the skill gaps and train them effectively to contribute better ways to the enterprise transformation initiatives.
Best Practices for Adoption of Generative AI
The following are the GenAI best practices that transforming the industry:
- Establish culture of responsible AI: Build use cases and minimum viable products, focus on governance, guardrails, prototype delivery systems, change management, and prioritization of use cases.
- Incorporate auditing: Perform Auditing that helps businesses develop and deploy policies to protect the business from risks such as copyright infringement and proprietary data leakages.
- Create Center of Excellence: Center of excellence upskill employees in generative AI, they can learn to adjust the prompts AI uses in the initial stages and fine tune in the later stages to address inaccurate and biased outputs.
- Democratize Ideas, Limit Production: Prevent employees from launching untested and unregulated AI projects.
- Prepare for dynamic data: Vast amount of dynamic data that GenAI creates include tables, code, and images. Enterprise leaders must work with agility to streamline data sources, talent, and technology.
- Bring in the Business: With GenAI, business executives to be intrigued, ambitious and vocal about what they could achieve with AI.
Where Should We Start with Generative AI
In most cases, the IT department of enterprises initiates the Generative AI adoption in response to business pressure to reduce the cost. They start the initiative with a lot of enthusiasm and over a period, it dies down on its own. This could be because of a lack of commitment from top management, shifting the focus to some other new initiative, poor planning and unrealistic expectations.
The following are the critical success factors to be addressed by Generative AI initiative across the enterprise.
- Build a business case
- Articulate the costs and risks of each potential Generative AI project, including the opportunity cost of doing nothing
- Democratize ideas, limit production. Prevent employees from launching untested and unregulated AI projects
- Allow employees to experiment without the ability to operationalize the use of generative AI
- Establish Centre of Excellence
- Upskill employees in Generative AI
- Building use cases and minimum viable products
- Prompt definition and fine tuning them
- Strategize and lead in governance
- Establish a Generative AI governance council to help guide enterprise decisions
- Ensure that Generative AI strategy to align with business strategy
- Clear communication of objectives of Generative AI to respective stakeholders
- Collect relevant and meaningful data
- Availability and time commitment from IT stakeholders and key SMEs/resources for information sharing, workshops, interviews, surveys, validation of findings, and related activities as per schedule
- Ask right set of questions very specific to customer pain areas leading Generative AI exercise
- Identify Dynamic data
- Check for existing data and use appropriately
- Prepare dynamic data. Dynamic data includes tables, images, videos, text, code etc
- Prompt identification
- Identification of Prompts
- Adjust the prompts AI uses in the initial stages
- Fine tune the prompts to address inaccurate and biased outputs
- Build Target Architecture
- Create target reference architectures
- Create Generative AI adoption Roadmap
- Define metrics
- Access to and active participation of all the stakeholders
- Bring in the business
- Establish a culture of responsible AI
- Maintain momentum
- Monitor the Generative AI initiatives through regularly scheduled reviews
- Demand regular updates on modernization projects
- Generative AI adoption as an ongoing process requiring regular evaluation
- Encourage employee interest in generative AI
Conclusion
The use of Generative AI across enterprises is becoming more and more widespread, possibly even trending toward industrialization.
Understand Generative AI fundamentals to identify business use cases. The enterprise AI Strategy guide in aligning AI initiatives to the enterprise business drivers. It needs to be aligned with enterprise business strategy. AI Strategy includes AI guiding principles, AI Governance, data management, people, process and technology. It provides list of activities and deliverables required for the successful deployment of GenAI solutions.
Train the people to promote Generative AI driven initiatives. Consider reskilling and upskilling employees to work with Generative AI effectively. Address and stay informed about emerging ethical guidelines and regulations related to AI.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Santosh Shinde of BTIS, Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd for giving the required time and support in many ways in bringing this article as part of Architecture Practice efforts.
About Author
Dr. Gopala Krishna Behara is a Enterprise Architect in BTIS Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd. He has a total of 28 years of IT experience. Reached at gopalakrishna.behara@hcl.com
Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd. He has a total of 28 years of IT experience. Reached at gopalakrishna.behara@hcl.com
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article/presentation are that of authors and HCL does not subscribe to the substance, veracity or truthfulness of the said opinion.
